Can Network Reading Continuity to Ground
Practical tips: CAN-Bus
-
Author: Timon Alferink
-
29 Aug 2017
A CAN-Bus protocol is designed to allow different devices to communicate with each other. This kind of communication is widely used in the Motorsport world. Now, there is a lot of (technical) information available on the internet. In this blog I will give you practical tips on how to use and test this for motorsport purposes.
Tip #1: Measure the resistance
The most common CAN-Bus issue is too much or too little termination resistance. In a low speed CAN each device should have a 120 Ohm resistor. In a high speed CAN-Bus (>100Kbit, used in automotive) only each end of the main loop should have a 120 Ohm resistor. Measure with a multi-meter the resistance between CAN-High and CAN-Low. Make sure the power supply is completely turned off. You should measure 60 Ohms over these 2 wires, because there are two 120 Ohms resistors in parallel (parallel resistance calculator). If there are 3 resistors in the wiring, you will measure 40 Ohms, and with 4 resistors you will measure 30 Ohms. Some devices have an internal resistor, but mostly these resistors are integrated in the wiring harness.
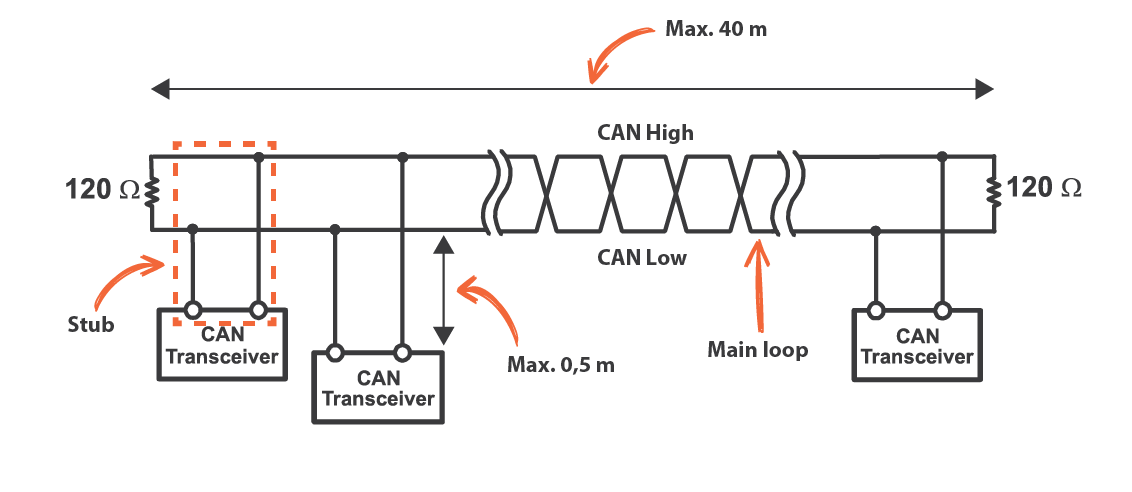
Tip #2: Check the speed of each device
In Motorsport, there are usually two (bitrate) speeds used: 500kbit/s or 1Mbit/s. As a rule of thumb 1Mbit/s can have a maximum cable length of 40 meters, where a 500kbit/s can have 100 meters. Try not to exceed 0,5 meter for each stub. If the stub is too long, it will result in data losses or error messages. From practical experience, most OEM CAN devices are at 500kbit/s. Motorsport devices are often set at 1Mbit/s. Always make sure you know the settings of each device connected to the CAN-Bus, or it will crash the communication. All devices need to run at the same speed.
Tip #3: Measure the voltages
Most of the time you will have a pin-out from a device (such as an ECU or display), so you can trace down the correct wire. But if you don't have a pin-out, and you are not 100% sure which wire is CAN-High or CAN-Low, you can measure the voltage of each wire. The CAN High wire usually fluctuates between 2.5V and 3.5V. The CAN-Low wire usually fluctuates between 2.5V and 1.5V. If you do not have a oscilloscope, you can measure the average voltage with a multi-meter. You will measure around 2,2V for CAN-Low and 2,7V for CAN-High.

Tip #4: Check the CAN-Bus load
There are several dedicated CAN-Bus monitoring tools available (such as Kvaser or PCAN-USB) which can show all raw CAN messages and bus load. Some ECU's or Displays have this kind of monitoring tools integrated as well. From own experience you need to try to stay below 60-70% load. You have a possibility of data loss or errors if you go above it. If you need to add more messages to the CAN-Bus, try to reduce the update frequency of some messages, or connect a second CAN-Bus.
Tip #5: Use multiple CAN-Busses
This is one of the most unknown/unused safety features in Motorsport. Put all important devices (ECU/Display/GCU/ABS) on 1 bus, and all secondary devices such as cameras or other 'unimportant' devices on a second CAN-Bus. Most of the latest generation ECU's and Displays have more than a single CAN-Bus. This will give you the possibility to receive signals on the first bus, and sent out on a second if needed. If a device such as a camera crashes the CAN-Bus, all important devices will still continue to work, and you can finish your race.
Overview:
- 120 Ohms on end of bus (only 2x 120 Ohms)
- Make sure all devices have the same bitrate speed
- Measure voltage of CAN-High and CAN-Low
- Do not exceed 60-70% CAN-Bus load
- Use multiple CAN-Busses to avoid communication errors
Thank you for reading this blog. If you would like to get more blogs on this subject, please share or comment below!
-
Share
-
Tags
- CAN-Bus
- Paddleshift
- Wiring
wigginsfrocceptere.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.kmpdrivetrain.com/paddleshift/practical-tips-can-bus/
0 Response to "Can Network Reading Continuity to Ground"
Post a Comment